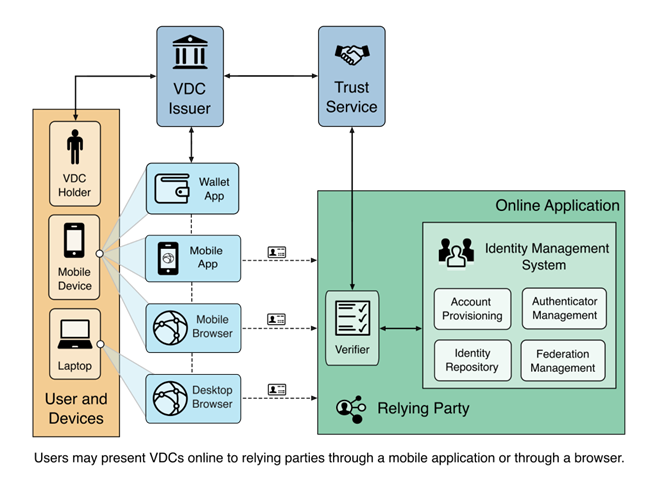
Key Participants in the VDC Ecosystem
The Verifiable Digital Credential (VDC) ecosystem involves several key participants that work together to enable secure, trustworthy digital identity verification. Each participant plays a specific role in the issuance, management, presentation, and verification of digital credentials.
Source: NIST Cybersecurity Insights Blog
Issuer
The Issuer is the authoritative entity responsible for creating and providing VDCs to individuals. Issuers are typically trusted organizations such as:
- Government agencies (e.g., DMVs issuing driver's licenses)
- Educational institutions (e.g., universities issuing diplomas)
- Professional organizations (e.g., certification bodies)
- Financial institutions (e.g., banks issuing account credentials)
The Issuer's critical functions include:
- Identity proofing the credential subject before issuance
- Generating the credential with verified information
- Cryptographically signing the credential to ensure its authenticity
- Managing credential lifecycle, including updates and revocation
Issuers establish the foundation of trust in the VDC ecosystem by validating identity information and creating cryptographically verifiable credentials.
Digital Wallet
The Digital Wallet is a software application that securely stores and manages a user's VDCs. It serves as the user's personal repository for their digital identity credentials and provides mechanisms for:
- Secure storage of multiple VDCs
- User authentication (typically using biometrics or PIN)
- Selective disclosure of credential information
- Presentation of credentials to verifiers
Digital wallets may be:
- Native applications provided by device manufacturers (Apple, Google, Samsung)
- Third-party applications available through app stores
- Specialized wallets issued by particular organizations or governments
The wallet acts as the user's control point, empowering individuals to manage which credentials they obtain and how they share their identity information.
Verifier
The Verifier is responsible for validating the authenticity and integrity of presented VDCs. When a user presents a credential, the Verifier:
- Cryptographically checks the issuer's digital signature
- Validates that the credential hasn't been tampered with
- Verifies that the credential hasn't been revoked
- Extracts the necessary claims or attributes from the credential
Verifiers typically implement standards-based protocols to communicate with digital wallets and process the credentials they receive. The Verifier may be integrated within an application or service, or it might be a standalone component that provides verification services to multiple applications.
Relying Party
The Relying Party is the entity that depends on the verification results to make access or transaction decisions. While sometimes conflated with the Verifier, the Relying Party represents the business function that requires the verified credential information. Examples include:
- Banks verifying identity for account creation
- Age-restricted services confirming eligibility
- Government agencies processing applications
- Healthcare providers accessing insurance information
The Relying Party's systems consume verification results and use them within their business processes, typically integrating with their identity management systems.
Trust Service
The Trust Service acts as a centralized infrastructure component that facilitates trust across the ecosystem. Its primary roles include:
- Maintaining registries of trusted issuers
- Distributing issuer public keys for credential verification
- Providing revocation information
- Establishing trust frameworks and governance
Rather than requiring each Relying Party to establish direct relationships with each Issuer, Trust Services create a "hub-and-spoke" model that simplifies integration and scalability. They enable a Relying Party to verify credentials from multiple Issuers through a single integration point.
Identity Management System
While not always explicitly mentioned as a distinct participant, the Identity Management System (IDMS) plays a crucial role within Relying Party environments. The IDMS handles:
- Account creation and management
- Authentication processes
- Access control decisions
- Integration of verified identity information into business processes
The IDMS typically consumes the output from the Verifier and incorporates it into the organization's broader identity infrastructure.
User Interaction Flow
A typical VDC interaction involves:
- The Issuer creates and provides a VDC to a user
- The user stores the VDC in their Digital Wallet
- When needed, the user presents the VDC to a Relying Party
- The Verifier validates the VDC's authenticity and integrity
- The Relying Party's systems consume the verified information
- The Trust Service facilitates verification by providing issuer validation
This ecosystem approach balances security, privacy, and usability while enabling trustworthy digital identity verification across organizational boundaries.